Hoare’s selecting algorithm is a textbook algorithm used to solve “find kth something”: kth smallest, kth largest, kth most frequent, kth less frequent, etc.
Time Complexity: Average O(n), Worst case O(n^2)
See 347. Top K Frequent Elements. Below, we solve this question with Hoare’s Quickselect.
Hoare’s Quickselect
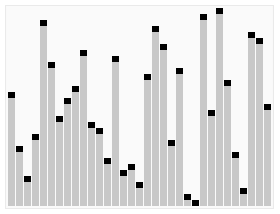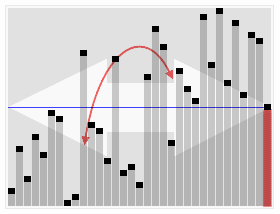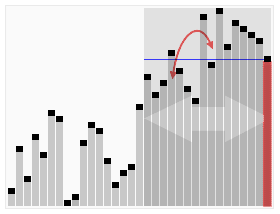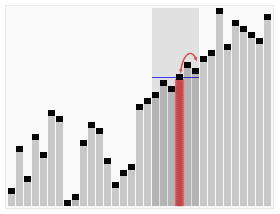
In a hashmap of <element, frequency>, select a random pivot point and use a partition scheme to place the pivot into a position where less frequent elements come to left side of pivot and more or equally frequent comes to the right.
If pivot index is N-k, there are k elements to the right side and all those are more or equally frequent elements, so return them. Else, choose the side of the array to proceed recursively.
Lomuto’s Partition Scheme
places elements >= pivot in the right side of pivot and elements < pivot in the left side.
- swap the
pivotwithlast element(or just start with the end element being pivot) - start a pointer from the left (index 0). Call this
store_index. - iterating from 0 to end, if the element is less than pivot val, swap the element with element at
store_index. If the element is >= pivot val, just pass. - After the iteration, swap pivot with element at
store_index(put pivot back in the right position).
Solution to 347. Top K Frequent Elements
class Solution {
private:
vector<int> unique;
map<int, int> count_map;
public:
int partition(int left, int right, int pivot_index) {
int pivot_frequency = count_map[unique[pivot_index]];
// 1. Move the pivot to the end
swap(unique[pivot_index], unique[right]);
// 2. Move all less frequent elements to the left
int store_index = left;
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
if (count_map[unique[i]] < pivot_frequency) {
swap(unique[store_index], unique[i]);
store_index += 1;
}
}
// 3. Move the pivot to its final place
swap(unique[right], unique[store_index]);
return store_index;
}
void quickselect(int left, int right, int k_smallest) {
/*
Sort a list within left..right till kth less frequent element
takes its place.
*/
// base case: the list contains only one element
if (left == right) return;
int pivot_index = left + rand() % (right - left + 1);
// Find the pivot position in a sorted list
pivot_index = partition(left, right, pivot_index);
//If the pivot is in its final sorted position
if (k_smallest == pivot_index) {
return;
} else if (k_smallest < pivot_index) {
// go left
quickselect(left, pivot_index - 1, k_smallest);
} else {
// go right
quickselect(pivot_index + 1, right, k_smallest);
}
}
vector<int> topKFrequent(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
// build hash map: element and how often it appears
for (int n : nums) {
count_map[n] += 1;
}
// array of unique elements
int n = count_map.size();
for (pair<int, int> p : count_map) {
unique.push_back(p.first);
}
// kth top frequent element is (n - k)th less frequent.
// Do a partial sort: from less frequent to the most frequent, till
// (n - k)th less frequent element takes its place (n - k) in a sorted array.
// All elements on the left are less frequent.
// All the elements on the right are more frequent.
quickselect(0, n - 1, n - k);
// Return top k frequent elements
vector<int> top_k_frequent(k);
copy(unique.begin() + n - k, unique.end(), top_k_frequent.begin());
return top_k_frequent;
}
};
